Edwards AE Bulletin, voice evacuation basics

File Preview
Click below to download for free
Click below to download for free
File Data
| Name | edwards-ae-bulletin-voice-evacuation-basics-6124098735.pdf |
|---|---|
| Type | |
| Size | 683.82 KB |
| Downloads |
Text Preview
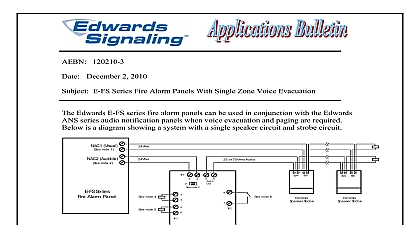
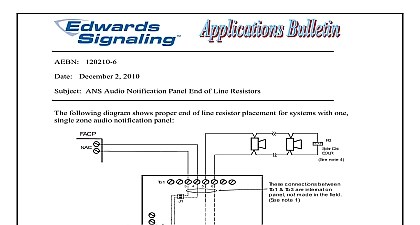
120210 9 December 2 2010 Fire Alarm Voice Evacuation Basics requires that fire alarm notification appliances in public mode produce a minimum of above ambient sound levels or 5dBA above the maximum sound level having a of at least 60 seconds Therefore in large areas or areas with high ambient noise you may think you have to always use very loud high wattage speakers Although this be true to some degree there more to it than that a difference between audibility and intelligibility While a single speaker may be loud to meet the audibility requirement it may be so loud that it not intelligible sounds or is uncomfortably loud to people near the speaker In some cases it may be better use multiple speakers of a lower wattage spread through out a covered area and you might need less power to do it some sound basics A sound output level using a dB scale does not take into account the hearing of the human ear If using this scale it must be associated with a ie 80dB at 1000Hz for it to have any meaning Although the general for human hearing is between 20Hz and 20,000Hz the human ear perceives the of different frequencies differently with the ear least sensitive to frequencies the upper and lower ends A 5,000Hz tone at 40dB for example would actually louder than a 100Hz tone at 40dB A sound output level using a dBA scale is measured using a filter that adjusts the A Weighting so that the meter responds closer to the way a human ear perceive the sound The same 100Hz tone at 40dBA would now sound as loud the 5,000Hz tone at 40dBA A 3dBA change in sound output is about the smallest change the human ear can requires twice as much power wattage to produce a 3dBA increase A 10dBA increase in sound output is perceived by the human ear to be approximately as loud requires 10 times as much power to double the perceived loudness Each time you double the distance from the source you loose 6dBA Conversely time you halve the distance you gain 6dBA Signaling Part of UTC Fire Security 41 Woodford Ave Plainville CT 06062 800 336 4206 Web www edwardssignaling com E mail signaling techsupport fs utc com 1 of 3 how can you save on amplifiers by using more speakers Here are a couple of examples 1 say an office area that 20ft across needs a minimum of 80dBA to meet the required level for evacuation You decide to use a speaker that produces 88dBA at 10ft using a watt tap Double the distance to 20ft and now you at 82dBA 88dBA 6dBA for the distance which meets the 80dBA minimum target let see what happens if you use 2 speakers mounted on opposite walls Each time reduce the speaker power by half the sound output only decreases by 3dBA So if the produces 88dBA at 10ft using the 2 watt tap it will produce 85dBA at 1 watt and at 1 2 watt Since the room is 20ft across 2 speakers on opposite walls each one 10ft tapped at a 1 2 watt will give the same coverage as 1 speaker tapped at 2 watts half the total wattage 2 need to cover an area like a machine shop or manufacturing plant that 40 feet across determine this will require a minimum of 87dBA throughout You got a speaker that produce 99dBA at 10ft using a 15 watt tap If you do the math 99dBA at 10ft equals at 20ft which equals 87dBA at 40ft 87dBA meets the requirements 99dBA is very loud and would cause discomfort to anyone standing near the when the system goes into alarm If you reduce the wattage the dBA will decrease it more comfortable for those people close to the speaker But you still need to get the coverage 87dBA minimum throughout the 15 watt tap you get 87dBA at 40ft So at 8 watts you would get 84dBA and at 4 you would get 81dBA But if you halve the distance to 20ft and mount a speaker at ends of the room you get the same 87dBA 81dBA 6dBA for halving the This would not only reduce the discomfort level to people near a single very loud it would also reduce the total wattage needed from 15 to 8 Signaling Part of UTC Fire Security 41 Woodford Ave Plainville CT 06062 800 336 4206 Web www edwardssignaling com E mail signaling techsupport fs utc com 2 of 3 should also be noted that when you are mounting speakers on opposite walls you should have any two be directly opposite each other The speakers should be mounted off center one another or staggered as shown below for best results looking down into room bulletin is intended to be a guide and the information given assumes ideal conditions room acoustics and speaker placement can effect sound dispersion Sound will travel in rooms with hard surfaces verses rooms with carpeting and curtains To achieve results dBA measurements should be taken to get ambient sound levels before starting design layout and then again after installation during an alarm condition to be sure you proper coverage Signaling Part of UTC Fire Security 41 Woodford Ave Plainville CT 06062 800 336 4206 Web www edwardssignaling com E mail signaling techsupport fs utc com 3 of 3