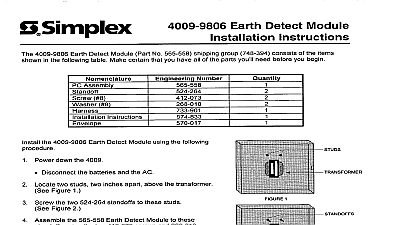
Simplex 4100-0136 Decorder Module Installation Instructions

File Preview
Click below to download for free
Click below to download for free
File Data
| Name | simplex-4100-0136-decorder-module-installation-instructions-0476823195.pdf |
|---|---|
| Type | |
| Size | 1.75 MB |
| Downloads |
Text Preview
implex Decoder Module 1993 Simplex Xme Recorder Co specifications Manuals Online were current es of publication are subject other change without notice 574 037 Manuals Online OF CONTENTS Devices Coded Operation and Terminology Timing and Rules Edge Detection DESCRIPTION Coder Loops Programming the Base Address DESCRIPTION Programming Unit Decoder Programming Procedure Programming Tips a Code Operator Panel Operation Discharge Caution Pulse Train Code Round Edge Pulse Train Code Round Method One Method Two Decoder Module Decoder Module Labels Reference Diagrams Conversion Select Switch SW9 Configurations 2 5 Manuals Online Manuals Online devices within a building device alarm circuit When connected activate a horn or bell to audibly reproduce a time pulsed code device encodes a panel a fire alarm control panel 4100 0136 Decoder Module stations The Decoder monitors Decoder Each coder and flow switches a 4100 family slave card that permits visual and or recorded annunciation of outputs of up to 8 coder loops with a total capacity of up to 250 devices devices such as pull interfaces with mechanical and electronic coded Decoder Module appears as two adjacent MAPNET channels on the 4100 bus and reports recognized codes the 4100 Master Controller as if the coded devices were addressable MAPNET devices This feature allow these points the full range of programming options available with the 4100 including annunciation and output from a printer Multiple Decoder Modules are allowed per 4100 system up to a maximum of five providing the system point capacity not exceeded Decoder Module it will monitor Programming Decoder consists of using the Decoder on board display and push button switches to enter each device code a MAPNET example CODE 2 3 2 equals Ml 1 codes of the devices field programmed recognize address CODED INITIATING DEVICES of coded devices can be encountered retrofit applications devices wheel type pull stations and flow switches microprocessor controlled the operation of the newer microprocessor controlled the earlier generation decoding codes from such devices as well can be defined that will allow the Decoder devices is usually intended to mimic the operation dynamically OPERATION AND TERMINOLOGY The following paragraphs describe coder operation and also define the terminology used throughout CODE is a series of ON and OFF signals that represent interpreted by a person listening to an alarm bell with each sounding of the bell being counted as part of a code of an alarm signal It is intended physical CODE PULSE pulses is a PULSE SPACE the ON signal and is represented as a single sounding of the alarm bell The interval between CODE D G T is made up of a series of code pulses and pulse spaces that can be audibly recognized as a digit space between code digits or D G T SPACE must be audibly the pulse time A of code digits and digit spaces make up the code A code can consist of from one to six digits For Alarm Code 3 7 2 as longer Alarm Code is repeated the pause between successive code rounds and must be audibly recognized as longer than the digit space termed one CODE ROUND The ROUND SPACE of four times each repetition defined as two successive code rounds that are stored VALlD CODE the Decoder nonvolatile EEPROM An UNRECOGNlZED CODE is defined as two successive code rounds that are not stored in the Decoder or part of a code that is interrupted by another code If a code after coding starts and transmits a continuous as an CODE A CODER TR